complex ovarian cyst cancer risk
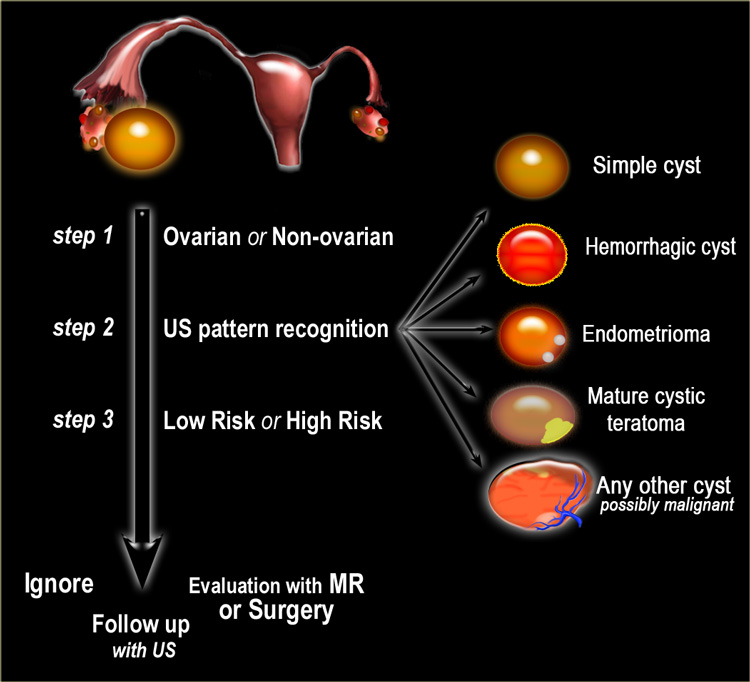 The Radiology Assistant : Roadmap to evaluate ovarian cysts
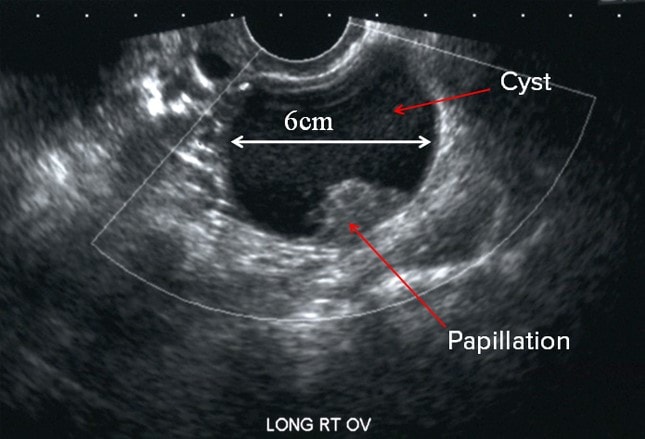
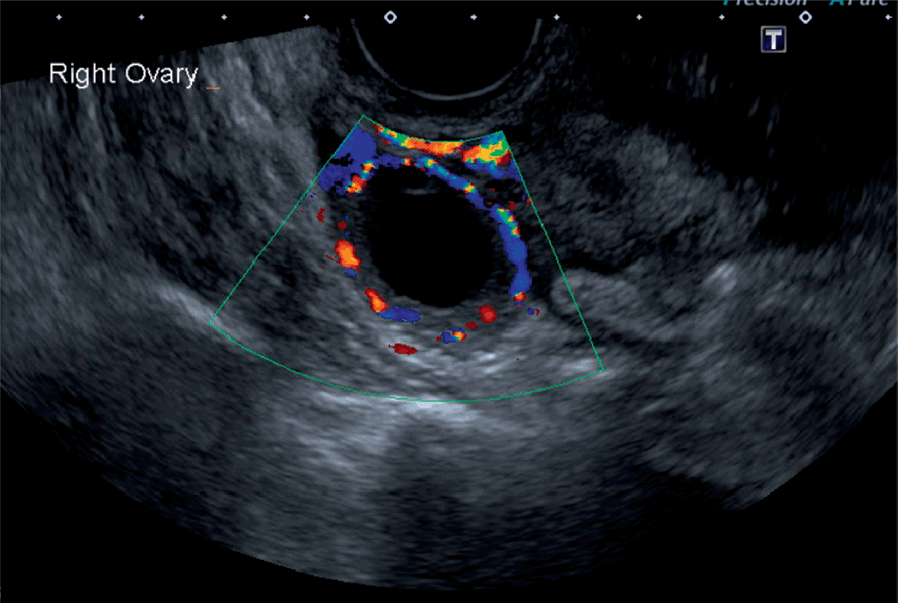
The Radiology Assistant : Roadmap to evaluate ovarian cystsFollow GE Health Care for Latest UpdatesSimple vs. Complex Ovarian Cysts and the Link to Ovarian CancerDifferencelating simple from complex ovarian cysts is key for gynecologists, as is determining the cancer risk they pose. Learn to identify these masses. The first concern of a practitioner when detecting an ovarian mass in a patient image is often to determine what kind of mass is and the possible impact on a patient's health. Your patient's first concern, however, is often to know whether that mass means cancer or not. Understanding complex ovarian cysts and being able to differentiate them from simple ovarian cysts is paramount for doctors and gynecologists. Being able to explain the risk of ovarian cancer in a simple and reassuring way for your patients is equally crucial. With the help of a growing number of imaging and modelling tools, health professionals are now better equipped than ever to treat ovarian cysts and masses and determine the likelihood that they can lead to cancer. Complex Ovarian cysts Ovarian cysts are sacks that develop in or in the ovary. There are two main types of cysts: simple ovarian cysts and complex ovarian cysts. Simple ovarian cysts are liquid-filled sacks, both in premenopausal and postmenopausal women. These sacks usually do not lead to cancer or a higher risk of it, and many simple ovarian cysts without treatment. In fact, it is estimated that less than one in 1,000 women with a simple ovarian cyst would develop ovarian cancer. Simple ovarian cystOvarian cystdenoma Unlike simple cysts, complex ovarian cysts are solid or irregular masses. Complex mass types include endometriomas, dermoids and cystadenomas. Complex masses will not necessarily lead to cancer either. Estimates that between 5 and 10 per cent of women have surgery to remove an ovarian cyst, but only between 13 and 21 per cent of women are cancerous. Gynaecologists can use ultrasound technology to distinguish between these different types of ovarian masses. Rules for the Identification of Ovarian Masses Transvaginal ultrasound, especially 3D ultrasound, can help doctors differentiate between benign simple cysts and potentially cancerous complex ovarian masses. For example, cysts containing papillary structures, solid areas and greater vascularity must be malignant. However, it may be difficult for doctors to differentiate between some complex and simple ovarian masses. The model (IOTA) tries to clarify these differences by providing practitioners with specific guidelines. The IOTA group's "simply rules" are a preoperative classification system for ovarian tumors that describes five common features of benign tumors and five common features of malignant tumors. Certain ultrasound machines, such as those with these IOTA protocols available on board, making ovarian mass evaluation even easier for clinicians. A growing body of research suggests that the use of these rules also has the potential to improve the attention of women with ovarian masses. For example, a meta-analysis of studies previously published found that IOTA rules could apply to , which could be transformative for the accuracy of the diagnosis of ovarian cancer. In addition, a prospective case-control study of 50 patients concluded that the sensitivity for the detection of malignancy in cases where the percentage was higher than 91 percent, with a specificity of more than 84 percent and a precision of more than 86 percent. Using IOTA ultrasound guides can help gynecologists make critical calls to differentiate between the types of ovarian cysts. Ensuring your patients that finding an ovarian cyst does not have to be a cause of stress, and that the diagnosis and more routine of what they think. IOTA Terms IOTA Simple Rules Protocol Voluson E10Using Ultrasound to Ease Cancer Concerns in Women with Postmenopausal BleedingLearn how doctors can effectively rule out cancer in postmenopausal hemorrhage within minutes with innovative ultrasound technology. This is VolusonTM SWIFTThis changes All Get Our Newsletter Sign Up for Latest GE Women's Health articles and updates. Related articles Sign up to get the latest articles and updates from GE Women's Health.© 2018 General Electric Company. Information on this website is intended only for health professionals.* Voluson is a trademark of General Electric Company. # All third-party trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Follow GE Health for latest updates

Simple vs. Complex Ovarian Cysts: The Link to Ovarian Cancer | Empowered Women's Health

Simple vs. Complex Ovarian Cysts: The Link to Ovarian Cancer | Empowered Women's Health
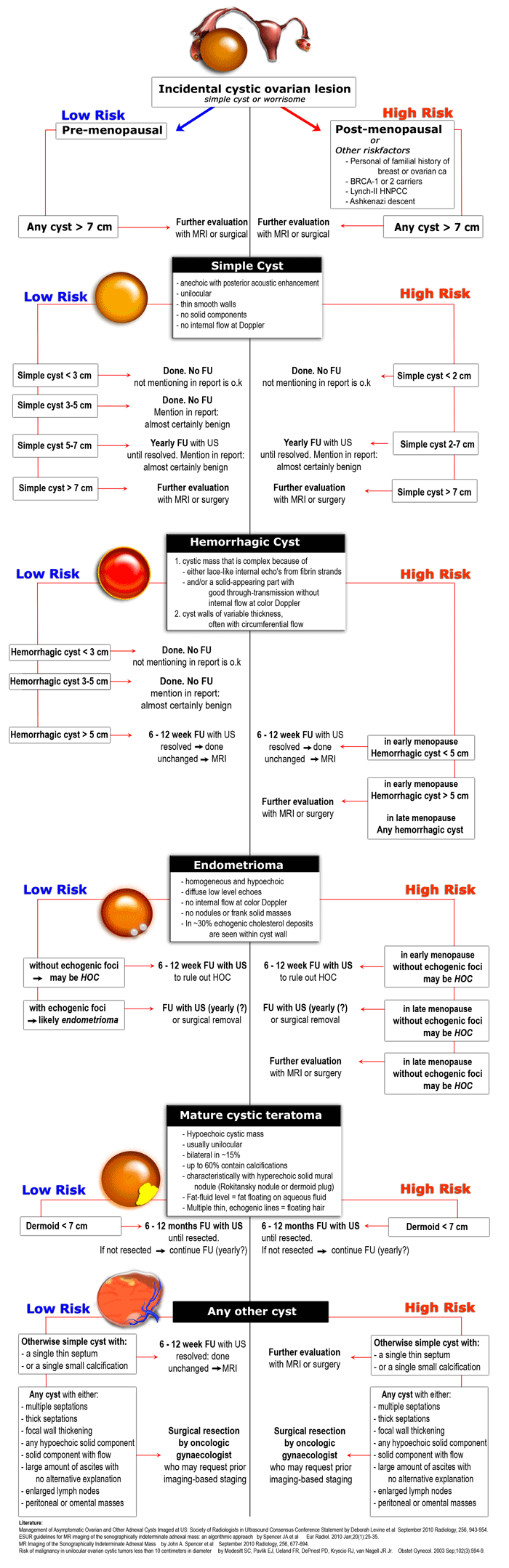
The Radiology Assistant : Roadmap to evaluate ovarian cysts
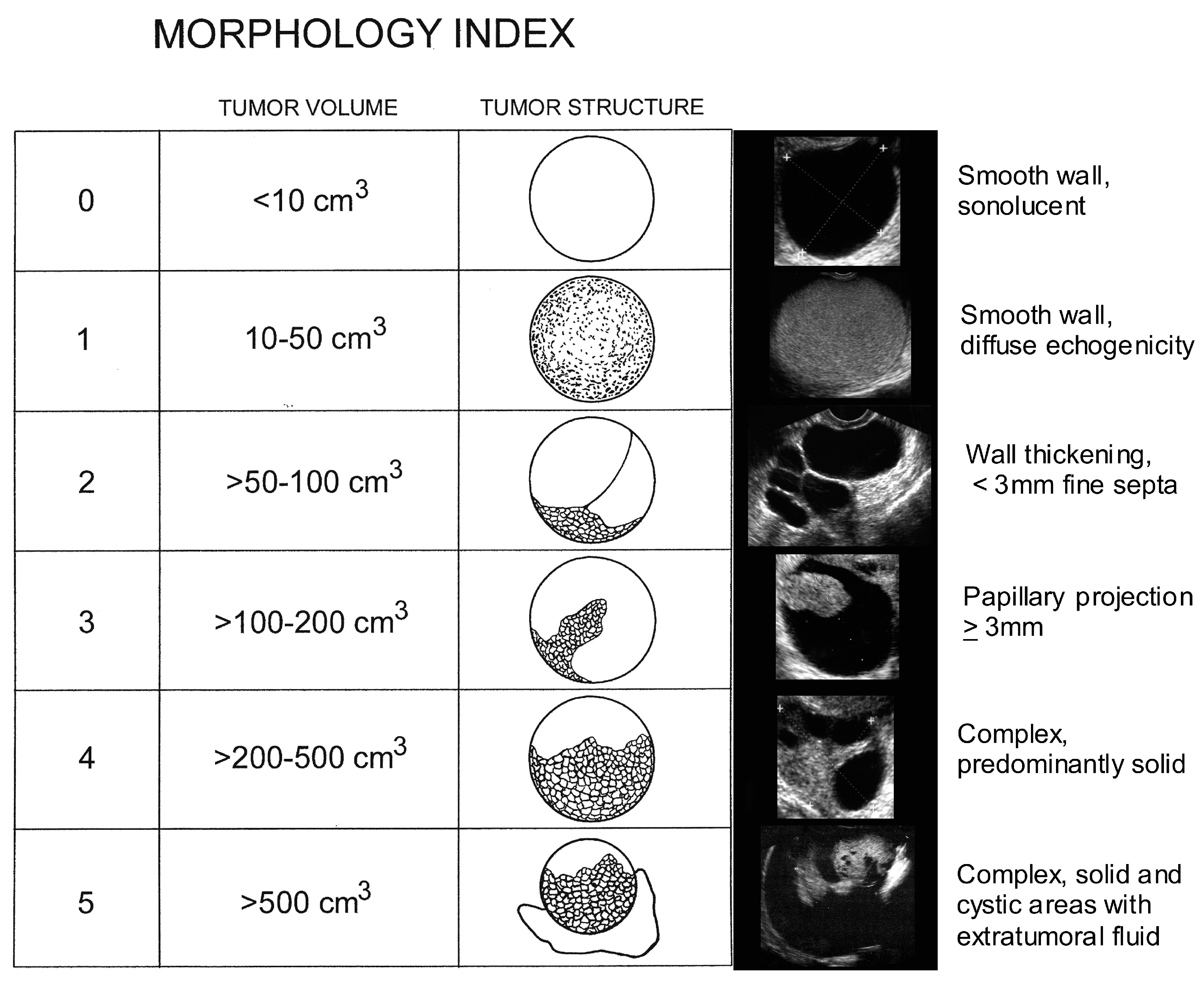
Diagnostics | Free Full-Text | Ultrasound Monitoring of Extant Adnexal Masses in the Era of Type 1 and Type 2 Ovarian Cancers: Lessons Learned From Ovarian Cancer Screening Trials | HTML
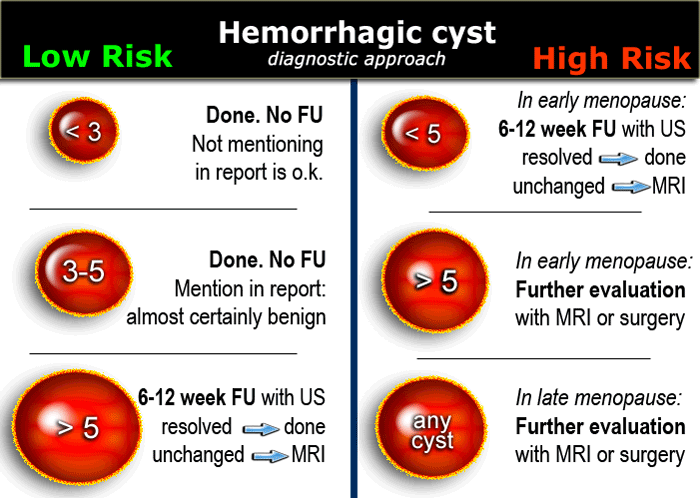
The Radiology Assistant : Roadmap to evaluate ovarian cysts
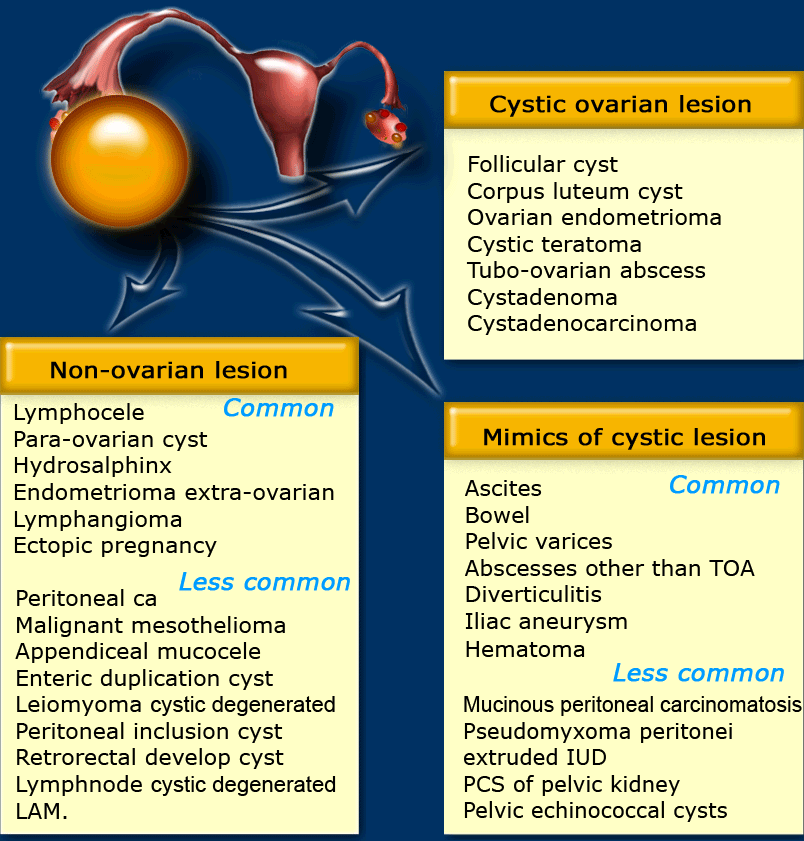
The Radiology Assistant : Roadmap to evaluate ovarian cysts
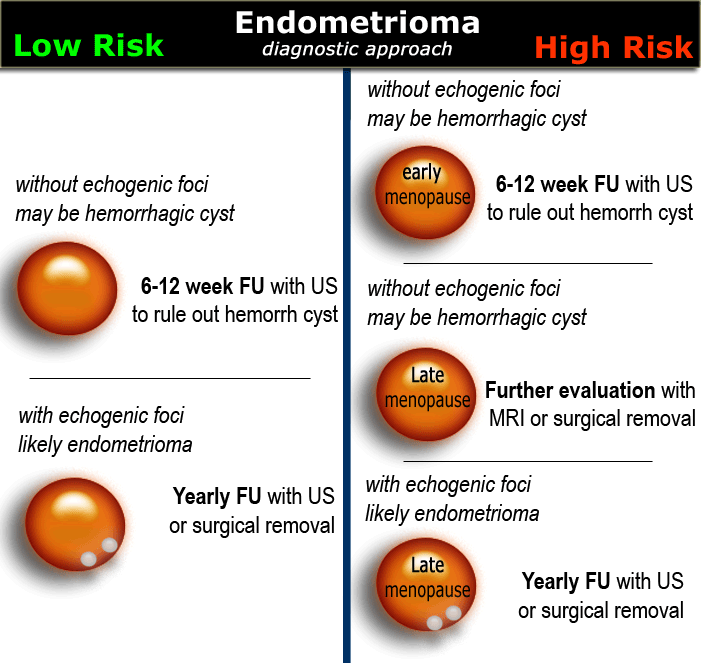
The Radiology Assistant : Roadmap to evaluate ovarian cysts

Simple vs. Complex Ovarian Cysts: The Link to Ovarian Cancer | Empowered Women's Health

The Radiology Assistant : Roadmap to evaluate ovarian cysts

Complex ovarian cyst: Symptoms, risks, pictures, surgery
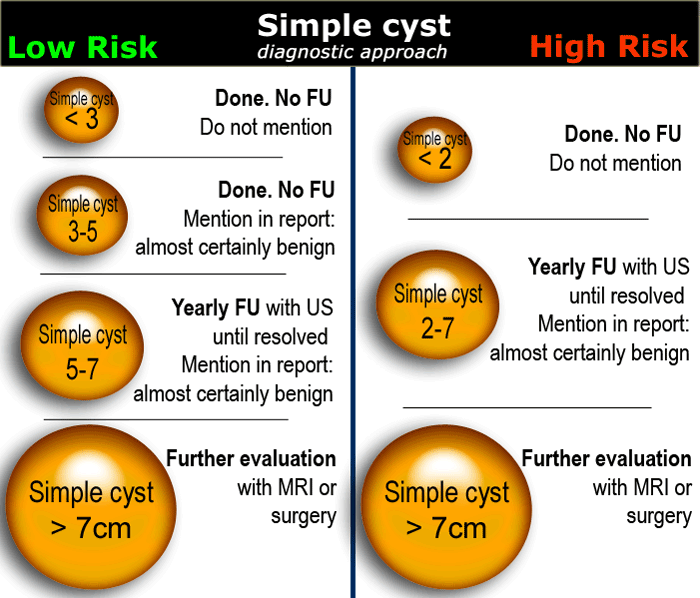
The Radiology Assistant : Roadmap to evaluate ovarian cysts
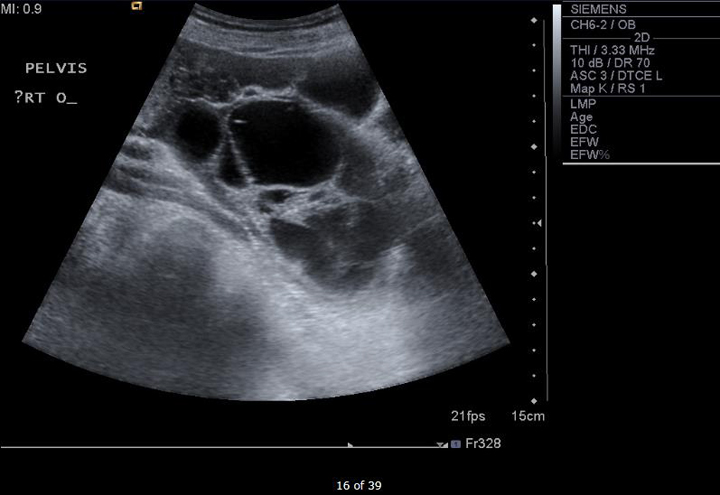
Ovarian Cysts
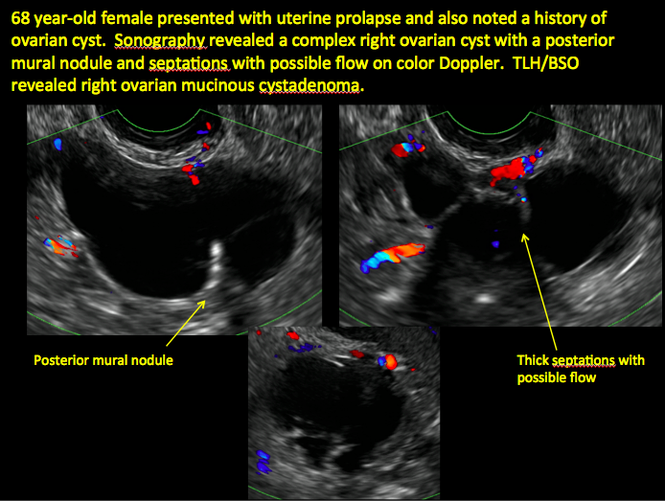
Imaging the suspected ovarian malignancy: 14 cases | MDedge ObGyn
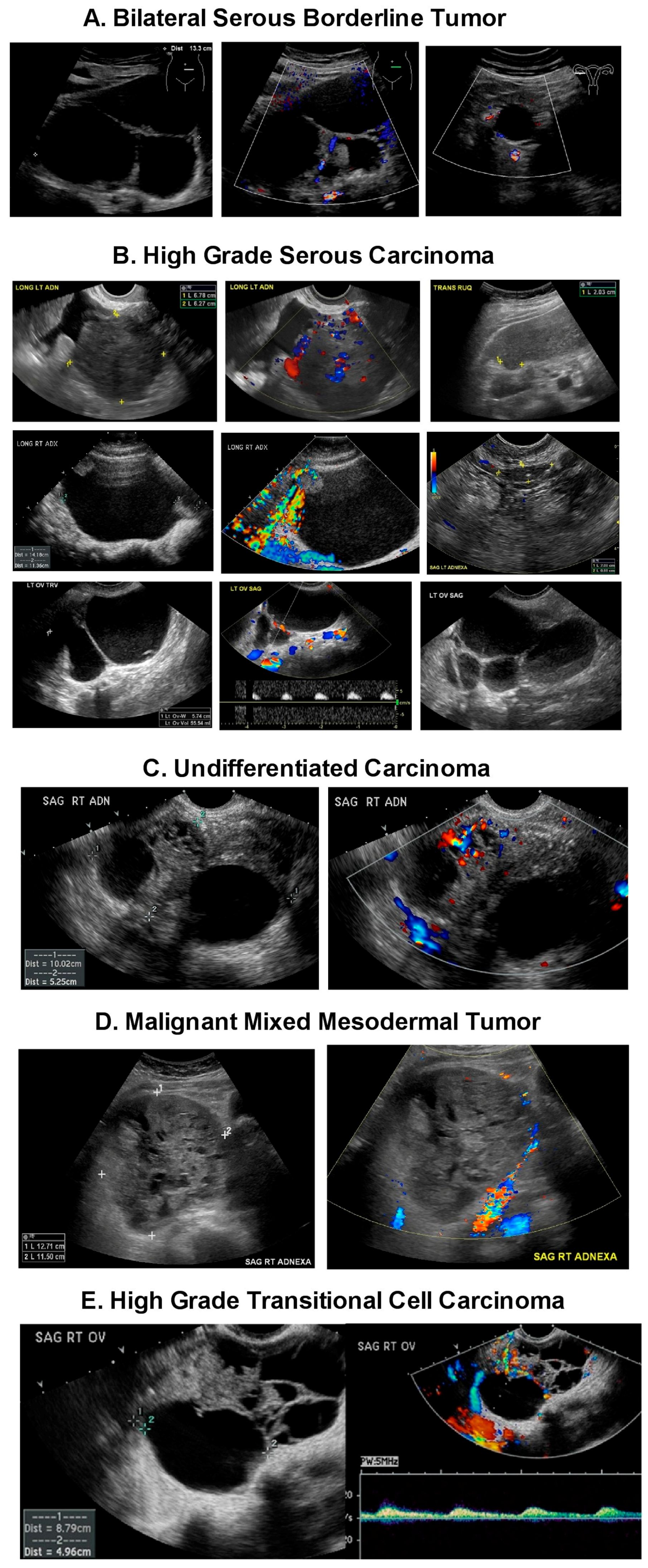
Diagnostics | Free Full-Text | Ultrasound Monitoring of Extant Adnexal Masses in the Era of Type 1 and Type 2 Ovarian Cancers: Lessons Learned From Ovarian Cancer Screening Trials | HTML
![Full text] Transvaginal ultrasonography in ovarian cancer screening: current pers | IJWH Full text] Transvaginal ultrasonography in ovarian cancer screening: current pers | IJWH](https://www.dovepress.com/cr_data/article_fulltext/s38000/38347/img/fig1.jpg)
Full text] Transvaginal ultrasonography in ovarian cancer screening: current pers | IJWH

Ovarian Cancer Risk Linked to Ultrasonographic Characteristics of Ovarian Masses - Clinical Advisor
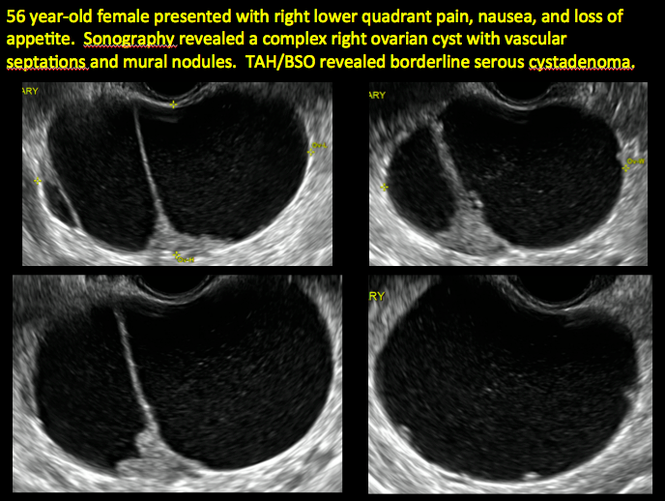
Imaging the suspected ovarian malignancy: 14 cases | MDedge ObGyn

Sonographic Assessment of Ovarian Cysts and Masses (Chapter 8) - Gynaecological Ultrasound Scanning
Ovarian Cysts

Pelvic ultrasound, showing a large complex ovarian cyst with layered... | Download Scientific Diagram

Indeterminate Adnexal Cysts at US: Prevalence and Characteristics of Ovarian Cancer | Radiology
Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian Cancer - Physiopedia
Ovarian Cysts: Functional or Neoplastic, Benign or Malignant?

Ovarian cyst - Wikiwand
Sonographic Assessment of Ovarian Cysts and Masses (Chapter 8) - Gynaecological Ultrasound Scanning

Ovarian Cysts in Girls | Children's Hospital Colorado

Treat Ovarian Cysts in 30 or 60 Days - ovarian cyst MRI a… - #cyst #MRI # Ovarian Naturally Eliminated Ovarian Cysts - More Than 15… | Ovarian cyst, Cysts, Radiology
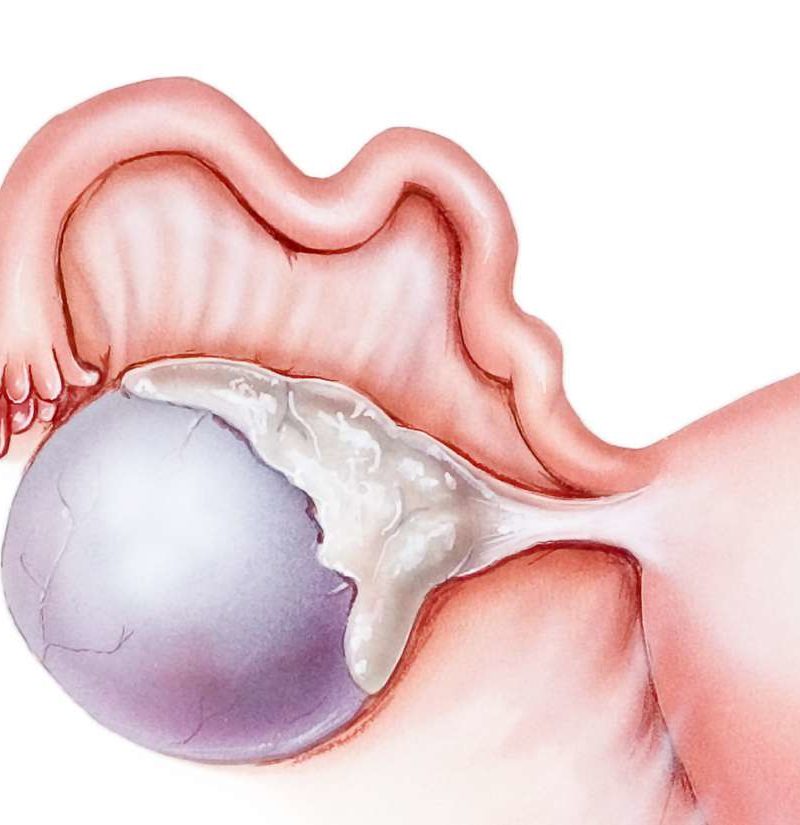
Complex ovarian cyst: Symptoms, risks, pictures, surgery
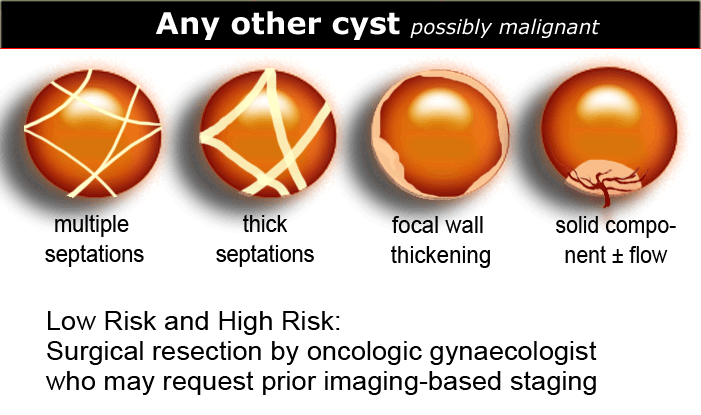
The Radiology Assistant : Roadmap to evaluate ovarian cysts

Imaging the suspected ovarian malignancy: 14 cases | MDedge ObGyn

Management of Asymptomatic Ovarian and Other Adnexal Cysts Imaged at US: Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound Consensus Conference Statement | Radiology
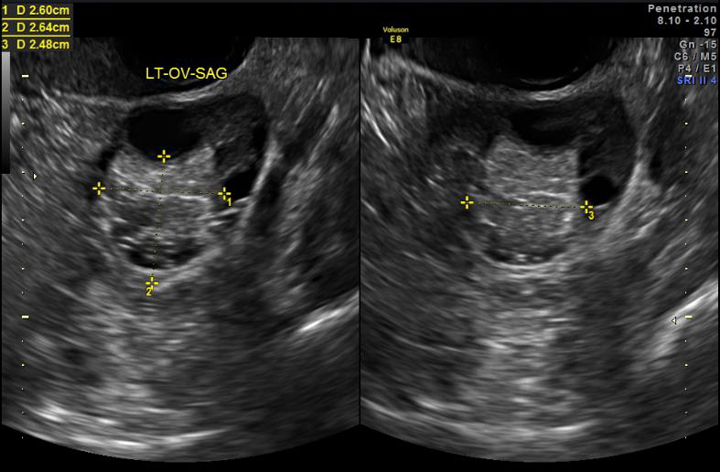
Ovarian Cysts
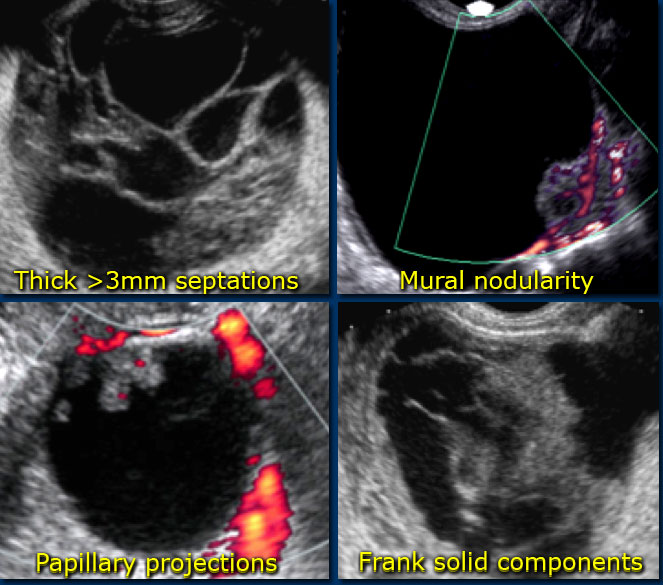
The Radiology Assistant : Roadmap to evaluate ovarian cysts

Ovarian cyst - Wikipedia

Simple Adnexal Cysts: SRU Consensus Conference Update on Follow-up and Reporting | Radiology

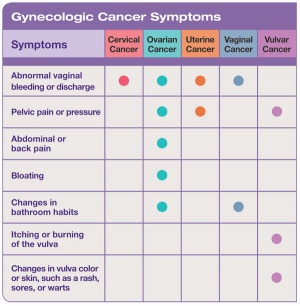
Ovarian Cyst Symptoms, Types, and Treatment
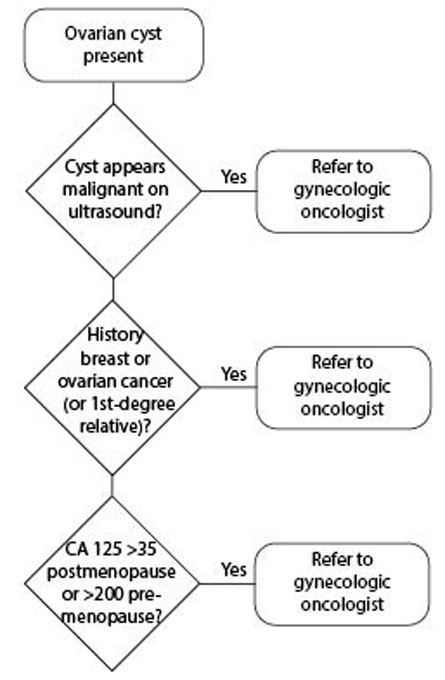
Ovarian Cysts

First International Consensus Report on Adnexal Masses: Management Recommendations - Glanc - 2017 - Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine - Wiley Online Library

Ovarian cysts | GPonline
Posting Komentar untuk "complex ovarian cyst cancer risk"